Eggs are renowned for their versatility and nutritional value, boasting both egg whites and yolks. The ongoing debate over which part is healthier often highlights the low calorie count, high protein content, and cholesterol-free nature of egg whites. For personalized nutrition advice, consulting a professional is recommended.
Egg, often hailed as a nutritional powerhouse, encompasses a spectrum of vital nutrients including protein, vitamins, minerals, healthy fats, and more. When delving into the egg, attention is typically drawn to its two components: the egg white and the egg yolk, igniting discussions on their respective health benefits.
Let’s delve into the nutritional profiles of both components to determine which one holds the nutritional edge.
Egg White:
- Low in calories and fat: With just 17 calories and 0.2 grams of fat per piece, egg whites are an ideal choice for individuals monitoring their calorie and fat intake.
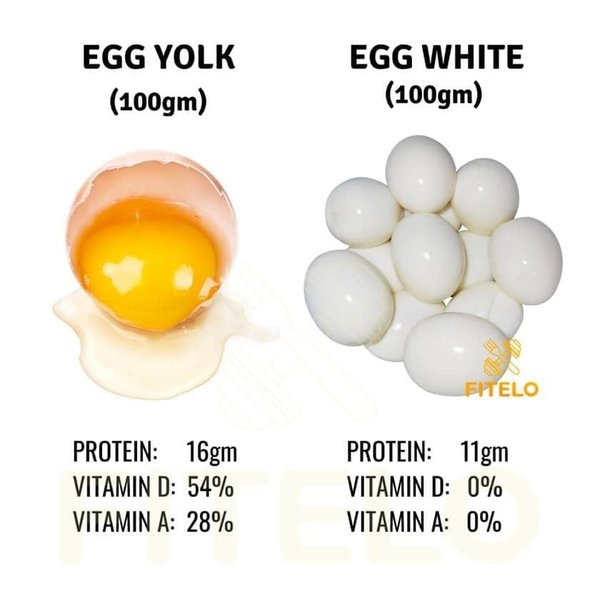
- High in protein: Packed with all essential amino acids crucial for muscle repair and growth, egg whites boast an impressive 11 grams of protein per piece according to experts.
- Cholesterol-free: Unlike egg yolks, egg whites are devoid of cholesterol, potentially advantageous for individuals with elevated cholesterol levels or heart disease risk factors.
However, it’s worth noting that while egg whites excel in protein content and lack cholesterol, they fall short in terms of essential vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats typically found in egg yolks. These include vital nutrients such as vitamins A, D, E, K, B12, riboflavin, folate, and essential fatty acids.
Egg Yolk:
- Rich in nutrients: Each egg yolk contains approximately 55 calories and a wealth of essential nutrients including vitamins (A, D, E, K, B vitamins), minerals (iron, phosphorus, zinc), and healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids.
- Abundant in choline: Recognized as a crucial nutrient for brain health, liver function, and metabolism, egg yolks are a notable source of choline, providing approximately 147 mg per yolk according to experts.
- Contains healthy fats: Egg yolks harbor unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can promote heart health when consumed in moderation. Each egg yolk contains a total of 27 grams of fat.
- Rich in iron: Studies suggest that 90% of the iron content in eggs is concentrated in the yolk.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that egg yolks are high in cholesterol, with one large egg yolk containing roughly 185 mg. While dietary cholesterol’s impact on blood cholesterol levels varies among individuals, those with specific health conditions such as high cholesterol or heart disease may need to monitor their intake.
In addition to nutritional considerations, egg yolks are recognized for their benefits for eye health, attributed to the presence of carotenoids which act as antioxidants protecting against retinal damage caused by free radicals.
In conclusion, both egg whites and egg yolks offer distinct nutritional advantages and disadvantages, and their consumption should align with individual dietary requirements. While the provided nutritional insights are valuable, seeking guidance from certified medical professionals or nutritionists is recommended for personalized advice.